Technical Info
General data
HOME > Technical Info > General data
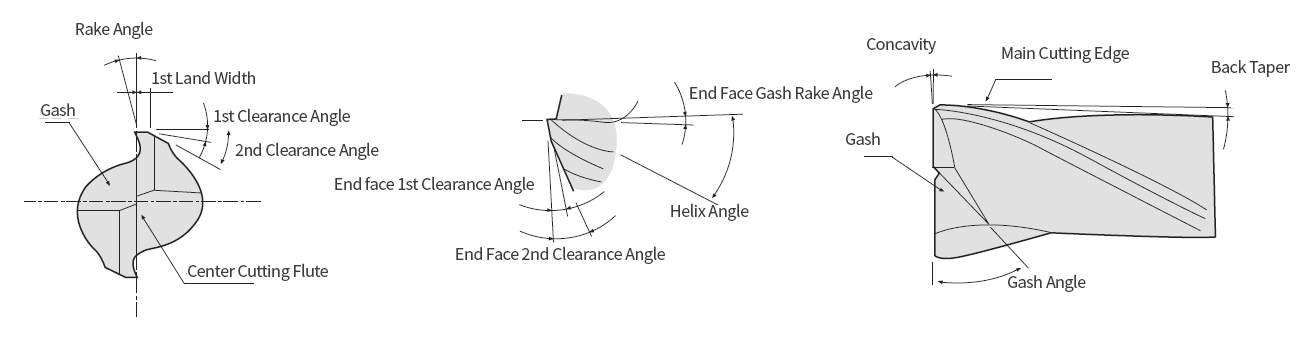
Endmill’s concept
Endmill’s concept
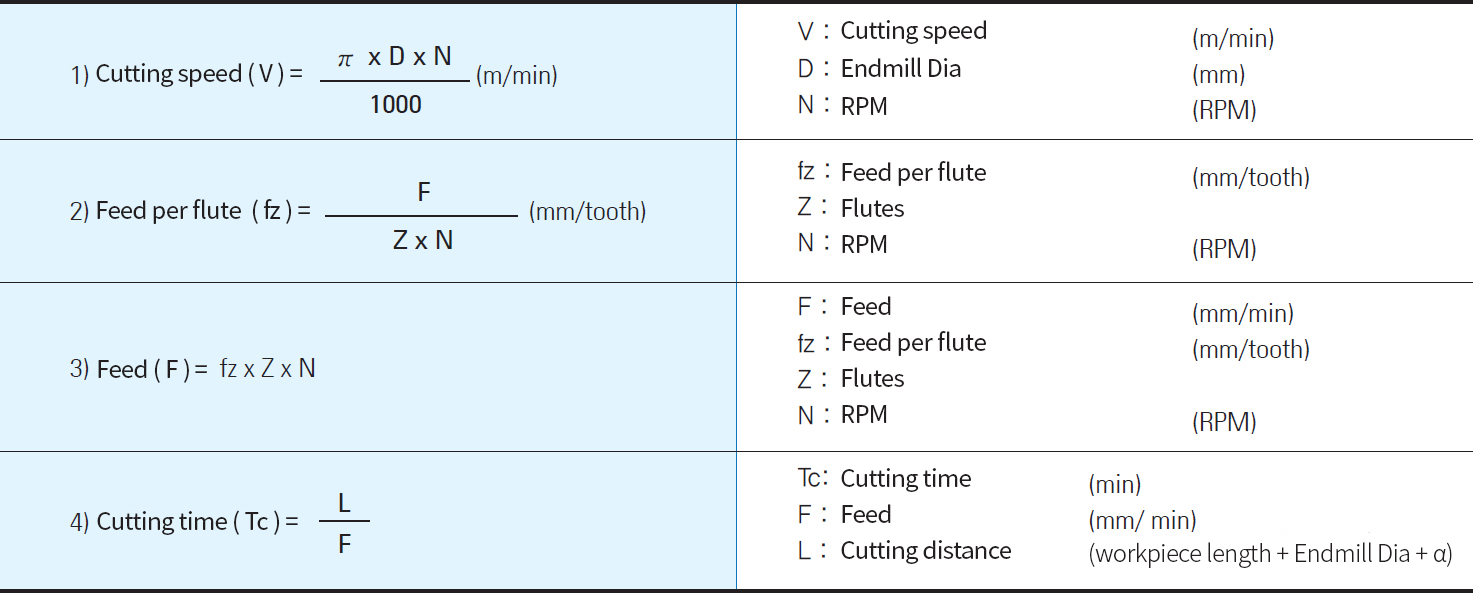
Cutting speed calculation
Cutting speed calculation
Endmill Regrinding
Endmill Regrinding
Regrinding timing
| Range of application | Endmill Dia | Abrasion loss |
|---|---|---|
| Finish machining | ~ ø10 ø 11 ~ ø30 ø 31 ~ ø50 |
0.05 ~ 0.1 0.1 ~ 0.25 0.2 ~ 0.35 |
| Roughing machining | ~ ø10 ø 11 ~ ø30 ø 31 ~ ø50 |
0.08 ~ 0.15 0.15 ~ 0.35 0.3 ~ 0.45 |
Way to regrinding
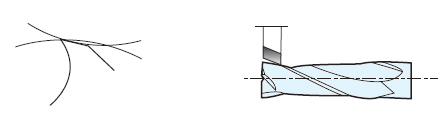
- (1) Concave type
- ㆍDemand to close Dia tolerance
ㆍFavorable machinability.
ㆍNeed to 2nd rake Clearance angle
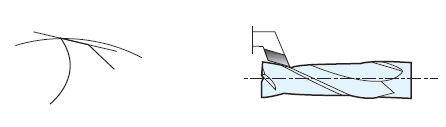
- (2) Concave type
- ㆍFavorable machinability
ㆍNeed to 2nd rake Clearance angle
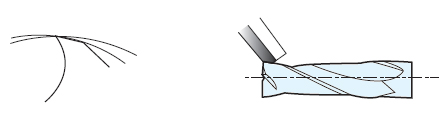
- (3) Eccentric Type
- ㆍFavorable Flute Diameter
ㆍExcellent Surface Roughness on workpiece
ㆍNot necessary for secondary clearance on rake
Honing
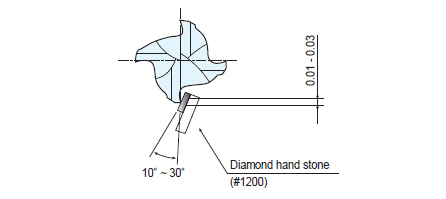
- Honing
- 1) Recommended for machining mold steel or high hardness workpiece.
2) When machining without honing, process it for 10 to 30 seconds with
an slotting of 0.01mm or less before entering the normal speed.
Endmill trouble shooting
Endmill trouble shooting
| Troble issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Broken |
|
|
| Wear and burr |
|
|
| Vibration during cutting |
|
|
| Defection for flute |
|
|
| Bad cutting performance |
|
|
| Poor chip emission |
|
|
| Burr on the surfacce |
|
|
| Shape faulty |
|
|
| Built up edge |
|
|





